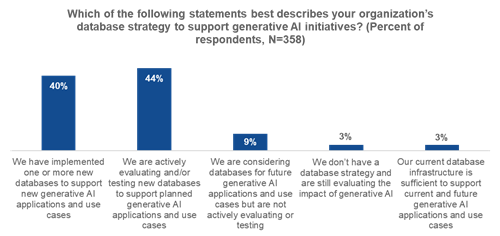
A wide majority (84%) of organizations are implementing or evaluating new databases to support generative AI applications. This data and the strong growth in generative AI application development show a continuous expansion of database technologies being implemented now and moving forward to support the many generative AI initiatives across organizational ecosystems (see Figure 1).1
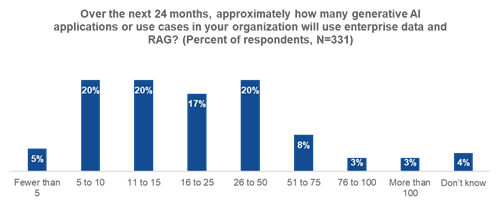
A significant contingent of organizations (71%) expected to implement 11 or more generative AI applications or use cases using enterprise data and retrieval-augmented generation within the next 24 months—with some planning to launch more than 50. This shows a massive ramp up in the plans for generative AI, including AI agents to empower decision-making, customer experiences, and even automate tasks, This represents many different types of enterprise data, all requiring database technology at the core to extract the important insights as the foundation for successful AI solutions built on trusted data (see Figure 2).
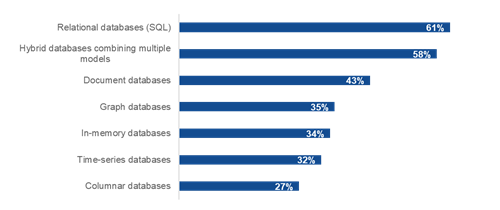
Organizations reported a diverse mix of database requirements to support their generative AI initiatives. This strongly supports the need for a converged database to manage the multi-models, formats, and management of structured and unstructured data with consolidated security and governance. As shown in Figure 3, the foundation of enterprise data for generative AI is a mix of many types of data with specific attributes that need to be addressed.
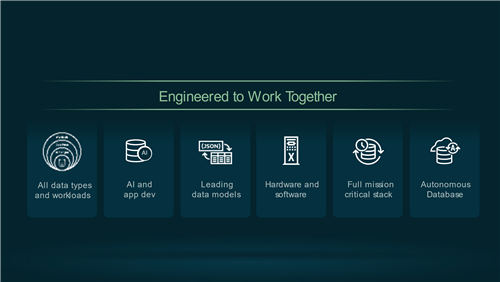
Instead of managing and integrating data across multiple specialized databases, Database Oracle 23ai and the Autonomous Database (fully managed version of 23ai) are engineered to deliver an integrated ecosystem that supports all data types and workloads. This comprehensive platform enables organizations to meet advanced AI and app development requirements by using Oracle AI Vector Search and AI Select in conjunction with leading large language models to ensure more accurate results, and developer productivity. By unifying hardware and software within a full mission-critical stack, Oracle enables consistent high performance, scalability, and security. The Autonomous Database further enhances this by automating data management tasks: provisioning, patching, backups, auditing, disaster recovery, and more, enabling businesses to focus on innovation while reducing operational overhead (see Figure 4).
In fact, one customer who presented at the summit noted that when searching vast media archives, speed is of the essence and shared that the AI Vector Search capability in Oracle Database 23ai deployed on Oracle Autonomous Database and running on Exadata is simplifying workflows and delivering a 7X vector search performance increase over their prior solution, improving the productivity of their post-production users.
Another customer uses Oracle Autonomous Database and AI Vector Search to analyze bacterial infections and provide tailored antibiotic recommendations. With this solution, they can rapidly analyze massive genomic data sets for advanced DNA sequencing, cutting diagnostic time from five days to under four hours and getting 50% better performance at one-third to one-half the cost of competitive offerings.
1. Source: Enterprise Strategy Group Research Report, Rethinking Database Requirements in the Age of AI, February 2025. All esearch references and charts in this brief have been taken from this research report unless otherwise noted.